In the last post, we discussed lasers. and began our venture into the realms of non-linear optics by considering the polarisation resultant from the anharmonic motion the dipole due to the perturbing electric field. In this post, we will continue where we left off, at 2nd harmonic generation.

Sum/Difference Frequency Generation
Two short wavelengths may be mixed to produce a long wavelength at the difference frequency. Conservation of energy and the phase matching condition are characterised via
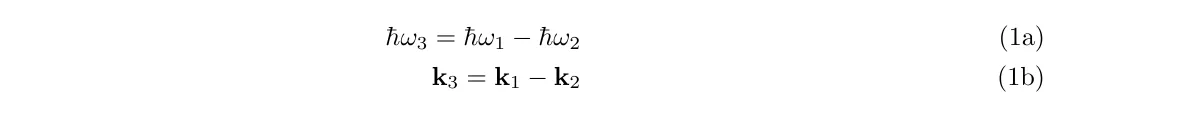
Two long wavelengths may be mixed to produce a short wavelength at the sum frequency. Conservation of energy and the phase matching condition are characterised via
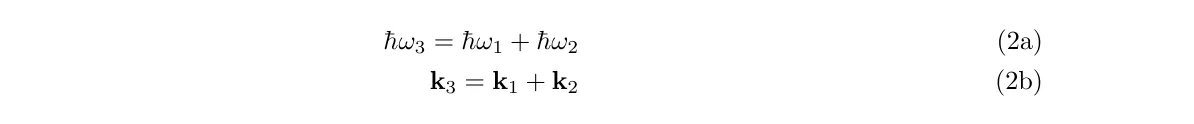
where we have

Optical Parametric Generation
This is effectively the opposite of sum/difference frequency generation. An intense optical pump is used in order to generate a 'signal' and 'idler' beam. Conservation of energy and the phase matching condition demand
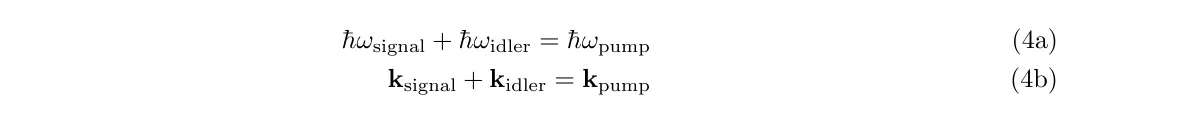
- If this is achieved through use of an optical cavity, the the process is termed Optical Parametric Oscillation.
- If, however, this is achieved using a very high gain optical medium, it is termed Optical Parametric Amplification.
2-Photon and Multi-Photon Absorption
Two-photon absorption is characterised by the simultaneous absorption of two photons of identical frequency, resulting in the excitation of an electronic state in the medium. This is a nonlinear process because since the transition rate is dependent upon the square of the intensity; indeed, it dominates over linear absorption at high intensities.
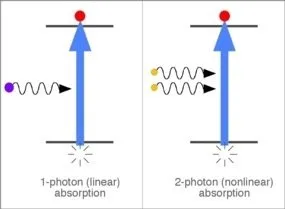
Other Important Non-Linear Effects
- High harmonic generation (e.g. X-rays from ultrafast laser pulses).
- Four-wave mixing.
- Kerr effect.
- Raman amplification.
Summary
- Classical optics has given us an understanding of how light propagates through materials.
- This allows us to design lenses, mirrors, prisms, gratings, etc. as well as more complicated instruments which involve compound optics such as microscopes and telescopes.
- We even get a basic understanding of how light of different frequencies interact with the electrons inside dielectric materials.
- Non-linear optics allows us to manipulate the wavelength of photons and create light at new wavelengths.